How to prepare for the Generative Search Experience (SGE) and Thrive with SEO
Understanding and conquering bots seems to be the next level that is becoming imperative for digital marketing and SEO professionals.
If very soon generative intelligence will save users the trouble of clicking from one link to another to find content that satisfies their search intentions and will deliver the information they need directly on the results page without having to consult sources, what is the future of brands’ digital presence? Will online sales decrease? Will organic positioning cease to be worthwhile? Will it even exist?
Throughout the pages of this paper, we will attempt to answer these questions and provide clues on how to act in a scenario of organic traffic loss, which is already beginning to be seen. The news, for better or for worse, in terms of efforts and investment, is that producing content will still be necessary, but not the type we are accustomed to publishing.
What is Generative AI in Search (SGE)?

Benefits of Generative AI:
-
Answering more complex questions with greater depth.
-
Deepening into topics directly from the search engine, as it allows you to ask questions right from the results page.
-
Personalizing the user experience through the context of previously conducted searches.
-
Accessing responses in creative and diverse formats tailored to your specific needs.
How SGE Works?
The SGE creates snapshots that help users quickly understand the topic they are inquiring about and provides related links for further exploration of their search.
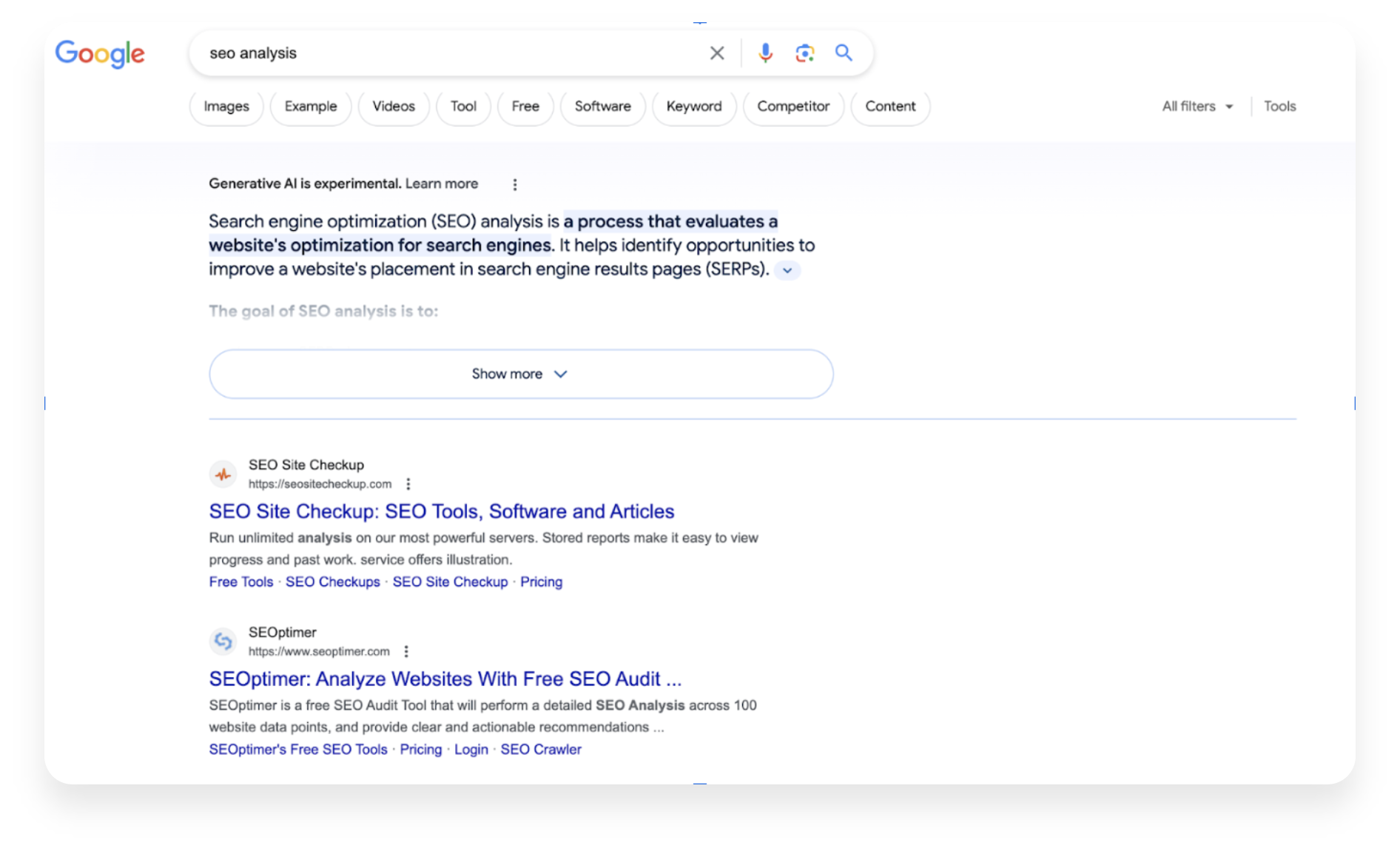
Likewise, the SGE facilitates theme tracking via the “ask a follow-up” section. Here, users can either click on other related questions suggested by the tool or type their own. This capability, enabled by generative AI, is particularly useful for asking more complex and in-depth questions about the search intent.
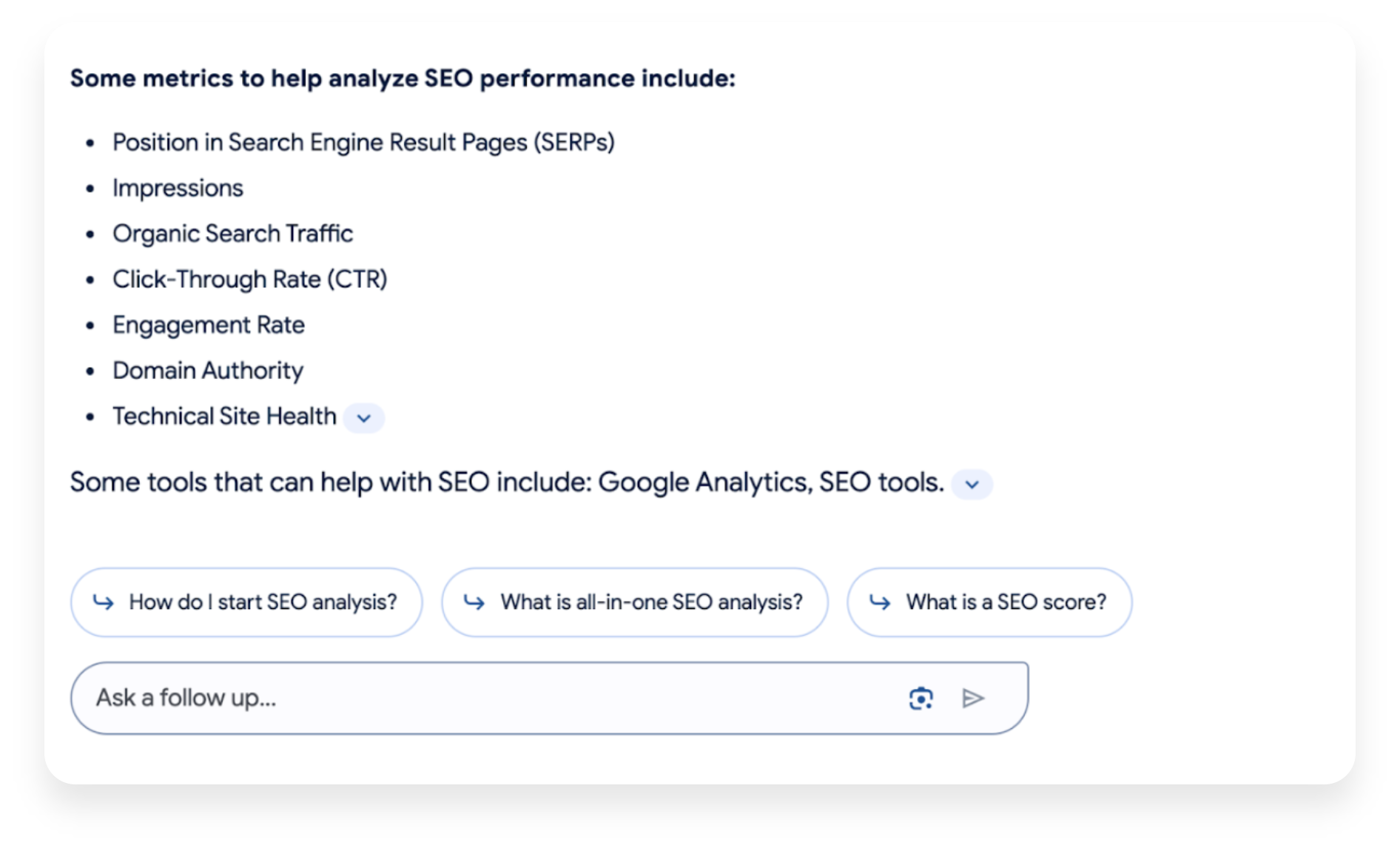
Through this process, users will gain access to vertical experiences such as local search or shopping, where the abundance of content can complicate decision-making. Utilizing AI and the available information, the SGE will deliver a response that considers account factors like ratings, reviews, prices, descriptions, and more.

Generative search is currently in an experimental phase, which means it’s not yet fully available to users. However, if your goal is to get ahead and see what the future holds, visit the Search Labs page where you can access some experiments, including Search Powered by Generative AI.

After accessing and clicking on “Get Started,” you must enable the following option in your browser.
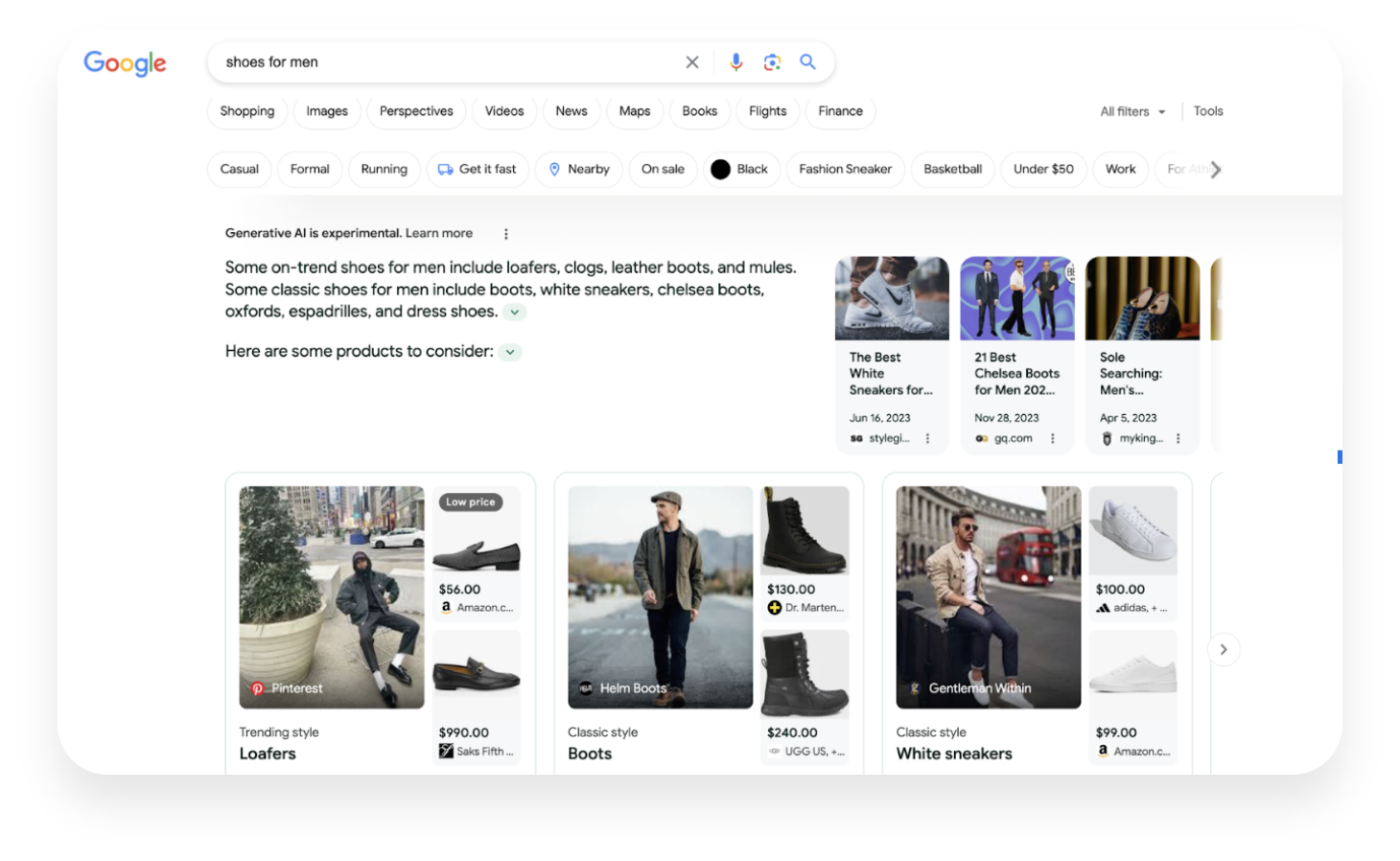
From that moment, and if enabled correctly according to your geographical location, you will start to see generative AI results in the searches you perform on Google. Here we show you an example with the search “shoes for men”:
How Will SERPs Change with SGE?
The competition to appear on the Search Engine Results Pages (SERP) will become even fiercer with the advent of SGE, alongside pay-per-click advertising, Rich Snippets, and other Google features. As Google’s experimentation continues, we will be striving for those coveted positions.
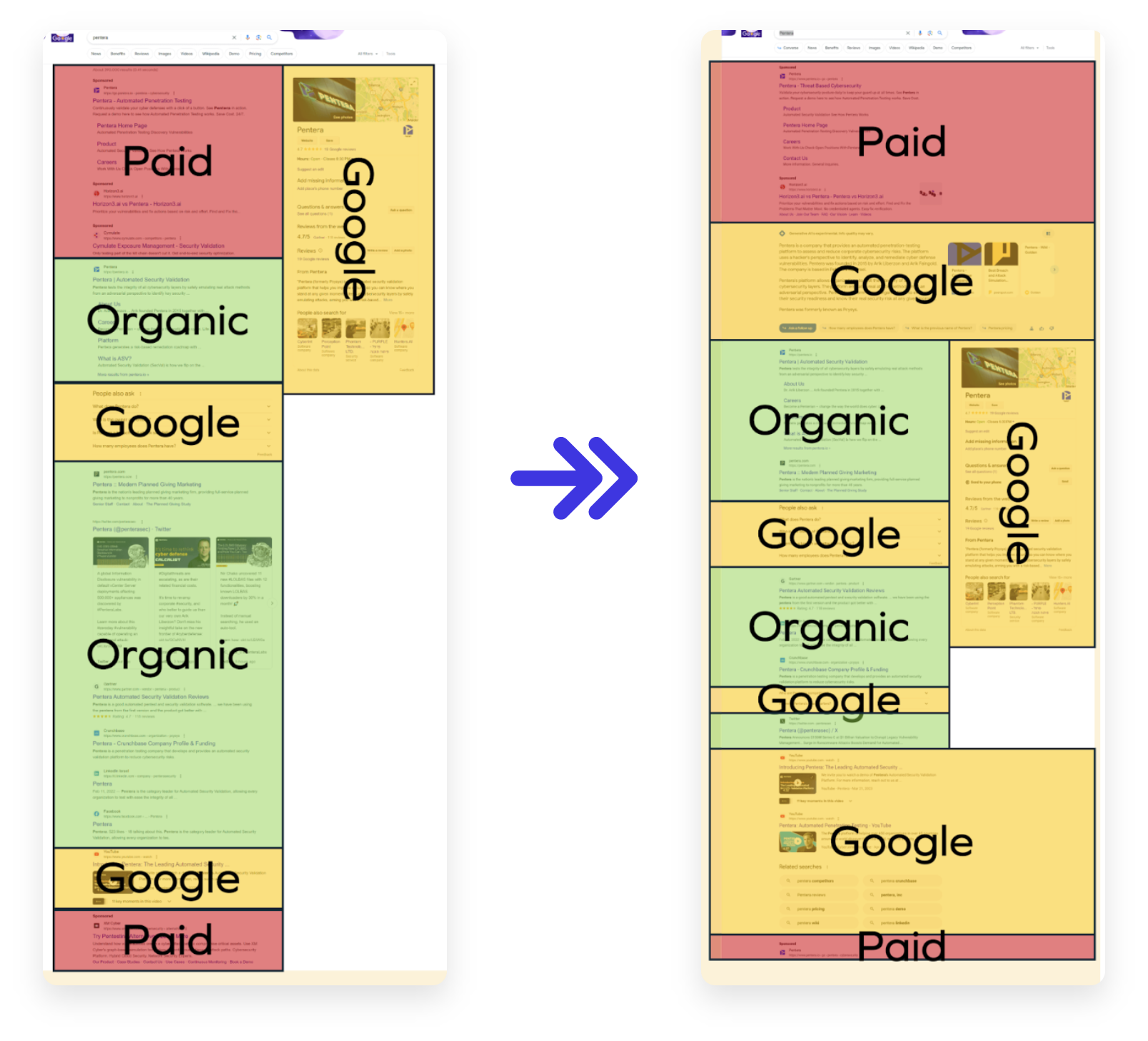
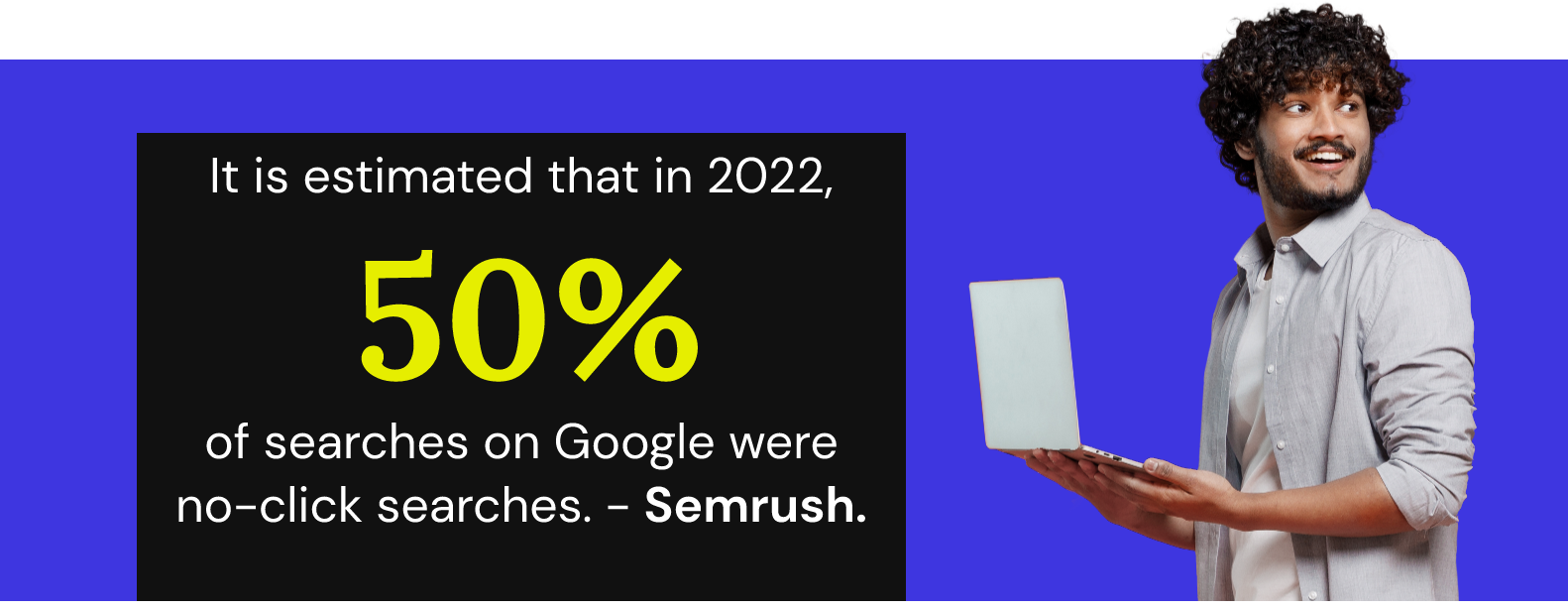
This demonstrates that while organic results previously accounted for between 40% and 50% of the SERPs, the space will now become even more competitive. Does this signify a new chapter for no-click search?
The no-click search era
The evolution of searches on Google, or any other search engine, has been consistent over the years, with Rich Snippets serving as one example. The primary desire of users is to find an answer easily and accurately, and this is where the era of no-click searches comes in.
No-click search refers to the ability to get answers on search engines without needing to click on any links. This means users find the answer to their questions without leaving the Google page, for example.
It’s evident that user behavior is constantly changing. The speed of updates and how businesses evolve are clear indicators of this. This is why their searches change as well. Users want answers more quickly without needing to visit a page where they might not find the answer as fast as they do with Google tools like “People also ask”, which feeds the search with frequently asked questions that other users are making on the same topic.
The core principle remains the same: to make users’ lives easier.

Will Google’s SGE Algorithm Kill Organic Traffic?
There’s a considerable amount of speculation regarding how Generative Search will impact digital strategies reliant on organic traffic and Search Engine Optimization (SEO) tactics. Indeed, there’s a palpable sense of panic and confusion circulating, fueled by apocalyptic notions predicting the demise of everything: clicks, organic traffic, websites, online ads, and even the viability of digital marketing as a profession.
However, the most prudent approach for marketing leaders, and even CEOs of companies, is to deconstruct the entire “generative intelligence” phenomenon into smaller components and analyze their individual impacts on the business. This paper aims to address the impact of the upcoming launch of the Search Generative Engine within Google on SEO and companies with established and authoritative domains. In the following paragraphs, we will delve into four key aspects:
Potential Changes in User Behavior
Plausible Decrease in Organic Traffic
Relative Importance of Owned Domains
Content: An Indispensable Strategy
Let’s dive into each one:

Potential Changes in User Behavior
Since ChatGPT has integrated into people’s daily lives, the dynamics between users and tools or interfaces have undergone significant changes. Conversational environments have permeated nearly all digital assets and transformed numerous work routines. Queries that were traditionally routed through Google can now be more promptly addressed by ChatGPT or its counterpart Gemini (formerly known as Bard), developed by Google.
Indeed, our discussion extends beyond mere inquiries or basic searches. We are delving into the realm of complete tasks performed by AI and its myriad applications, including ChatGPT itself. These tasks encompass content writing, copywriting, and design – essentially, all activities associated with the creation of digital assets.
Even more pertinent is the accessibility of AI-curated content from the internet, accessible to users using Chat GPT within Bing or through Gemini, already integrated with Google.
In essence, conversational searches and generative results have become ingrained in digital habits. They provide answers to the What, Who, Where, When, Why, and How of almost everything without necessitating any clicks. Hence, one preliminary conclusion that emerges is the inadvisability of expecting organic traffic from this type of content and inquiries.
Plausible decrease in organic traffic

It is highly probable that the decline in organic traffic is inevitable, as informational queries will increasingly depend on aggregating content from various sources until AI can furnish accurate and curated answers for users.
For instance, let’s contemplate someone seeking information on the economic impact of global warming, which constitutes an informational query.
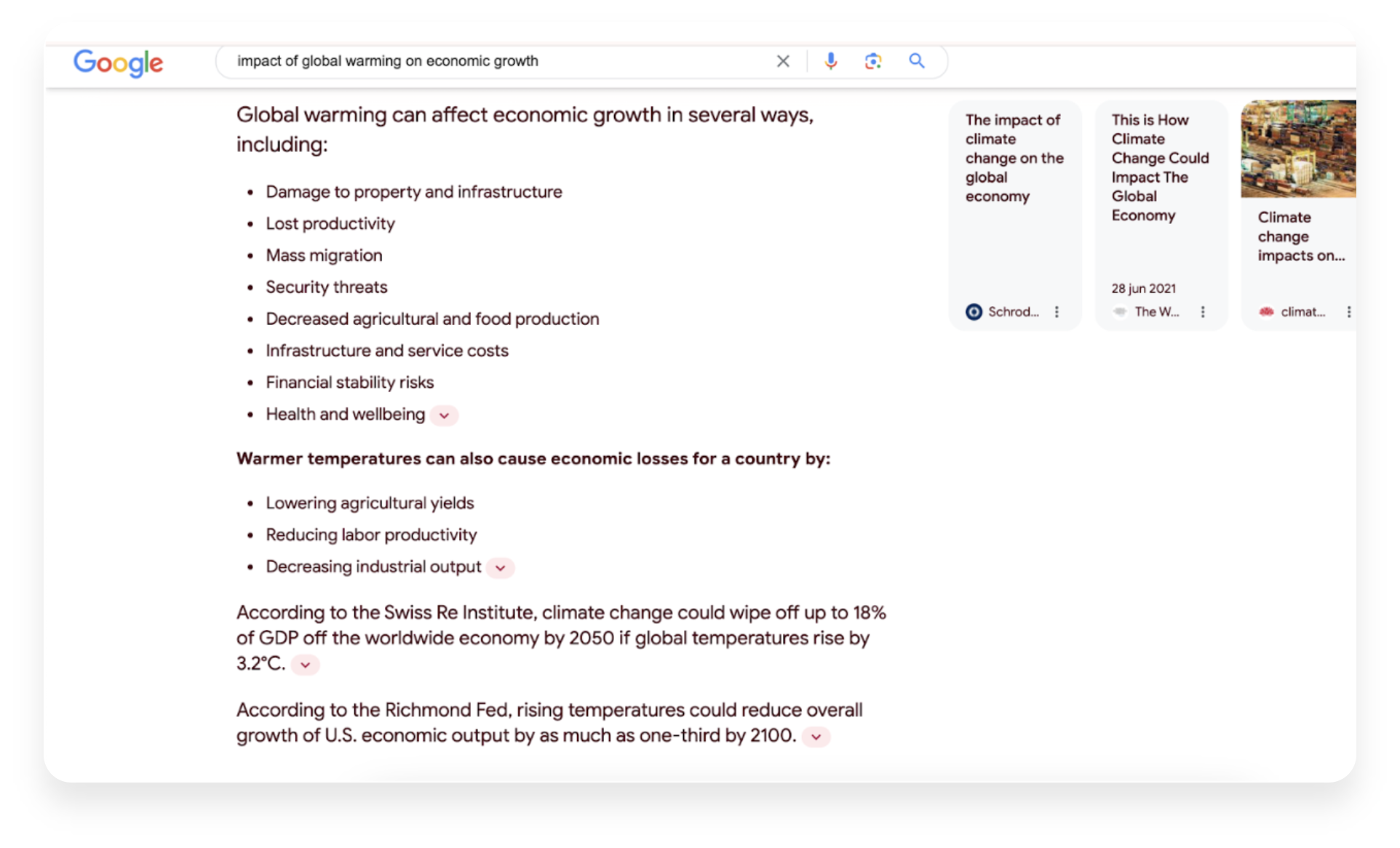
Given such an explanation, the likelihood of users clicking on the web pages displayed in the right corner of the image is extremely low.
That being acknowledged, what might be the business’s repercussions if it loses traffic stemming from informational searches? It is plausible to assert that a certain portion of the decline in clicks would not necessarily translate into actual revenue.
Now, consider the scenario where the same user from the previous example attempts to search for a different broad query, such as “how to get a mortgage.”
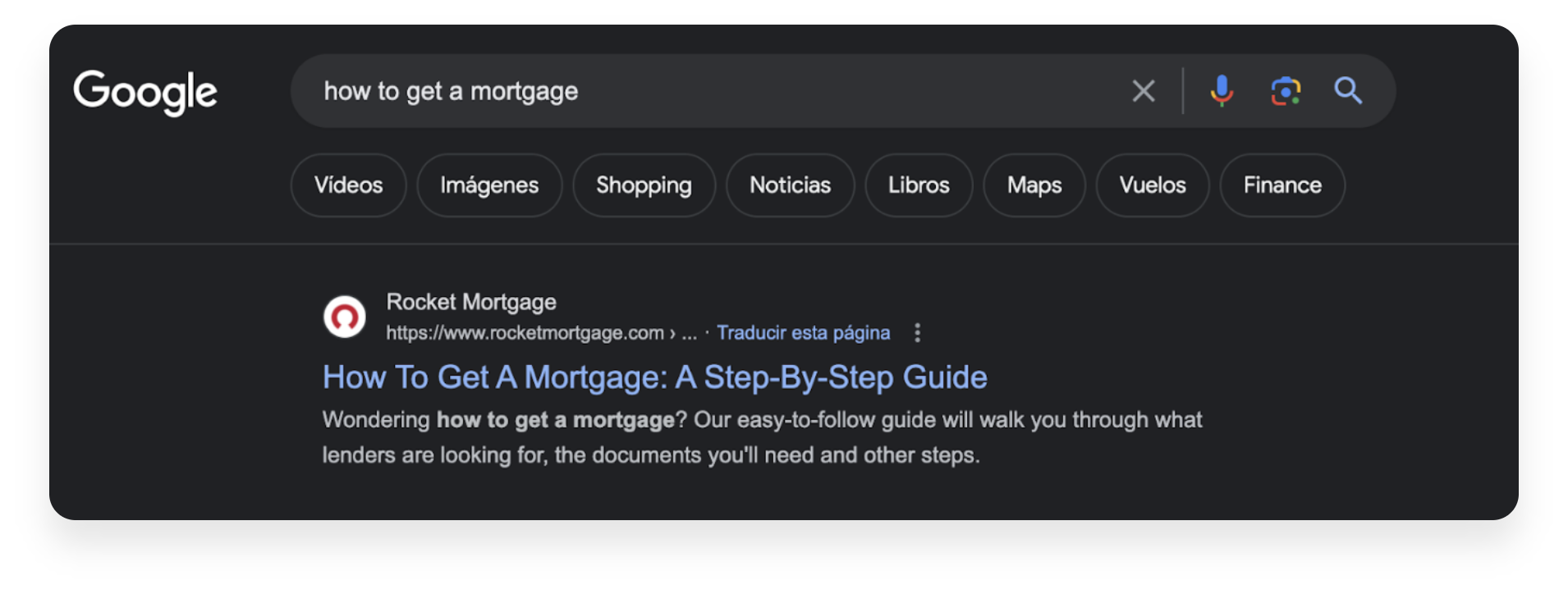
In this particular case, Rocket Mortgage, occupying the first position, is poised to secure the visit. However, there’s no doubt that Google, with its Search Generative Experience, will intensify efforts to address nearly all informational queries with generative functionalities.
Nonetheless, according to David Shapiro, Senior Vice President of Earned Media at NP Digital, “SGE’s impact is undoubtedly significant, but the perceived impact of SGE will likely exceed the actual impact. That’s because SGE might bear the brunt of responsibility for other changes occurring in the broader search landscape.”
This trend can be attributed to several factors. Firstly, the click-through rate (CTR) for queries related to the 6 Ws has been steadily declining over time. Secondly, Chat GPT has been diverting searches from Google since its inception, particularly after its integration into the new Bing search engine.
Relative Importance of Owned Domains
Considering that the decline in organic traffic is inevitable and has been experienced for some time now, the next question arises: What will happen to business websites? Will they become obsolete digital assets? What remains of the value of the domain, earned through authority and brand strength?
For now, the first response is hopeful: the bots will continue to search the internet, and the results with generative intelligence will continue to be built from that same source. Therefore, the natural place where the contents of brands, their products, and their services should continue to reside is their websites. Additionally, it is plausible to think that no search engine will be willing to give up the revenue flow from advertising exposure on URLs of internal pages and homepages across the web, at least until another source of monetization becomes more appealing.
Regarding the second issue, which is the prominence of one’s own domains, the answer is slightly different: while organic traffic to websites may decrease, it doesn’t mean that users will stop searching. Hence, the struggle for visibility of one’s own domain expands into a more general strategy, where the goal is to ensure that after searches, prospects and customers see the brand regardless of the domain that exposes it. This is why digital public relations become even more relevant. What do they consist of?
It consists of allocating efforts not only to rank in the top positions but also to be mentioned as a brand, product, or service on domains with higher authority and positioning. For potential customers, the experience with the brand will hold great value, in the sense that seeing it referenced on multiple sites will generate trust and credibility. And for the brand, a strategy of this kind will significantly amplify its reach.
Let’s suppose we are a chain of small appliance stores and we want to position ourselves and sell air fryers.
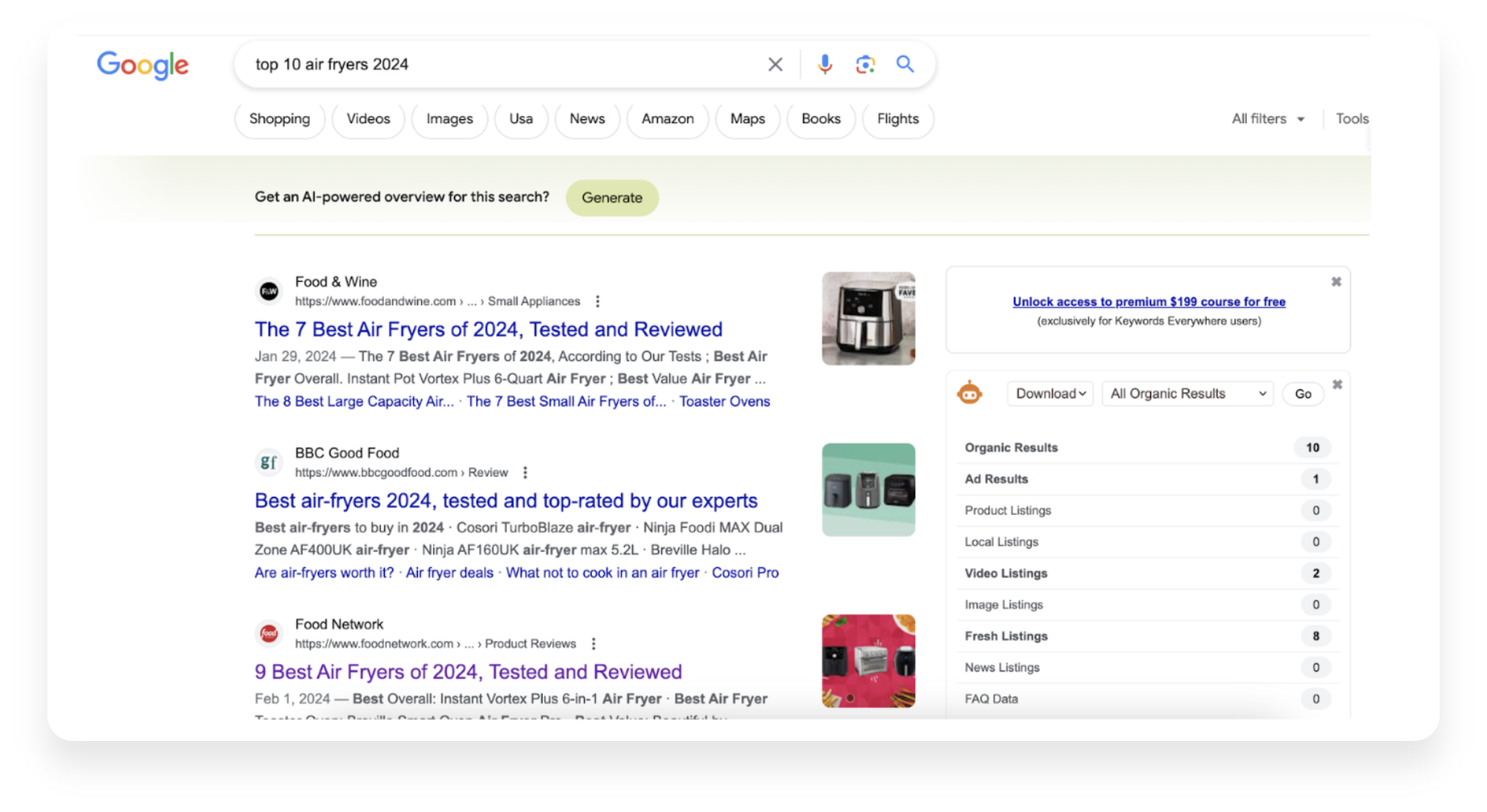
The first thing we can say with these results is that it can be difficult to occupy the first portion of the results page with this search. If we return to the issue of public relations, we could contact the editor of Food and Wine or BBC Good Food to try and review our air fryers.
But we are talking about generative search. So it is necessary to see what happens when we do a search by activating SGE in Google.

What happens is that the SGE tool brings us other sources of information different from those shown in the previous search, without SGE, whereby we gain two types of trusted sources for the search engine: those it uses to produce generative results and those it uses to display sites in the traditional results page. And in this way, the digital relationship strategy can be enriched.
HubSpot coined this tactic under the name “Surround Sound SEO,” and its discovery stemmed from analyzing, in real life, how someone makes the decision to buy something new. In the physical world, we can replicate the case of air fryers as follows: a young woman is moving house and asks her office colleague which is the best air fryer to buy. Her colleague responds that she has tried several and that the best one, without a doubt, is the Cosori Pro.
It’s likely that this name doesn’t resonate with her and she may soon forget it. However, the next day, she asks the same question to her gym mates, and three out of five members of the group recommend she buy the Cosori Pro.
If, days later, she finds the same response in the group chat with her university friends, it’s highly likely that our protagonist’s decision will be to buy the Cosori Pro. HubSpot maintains in this article that as the number of mentions of a product from multiple sources increases, so does the probability of purchase.

Content is not something to quit doing
Let’s continue with the case of the best Air Fryers to buy in 2024: we already have the recommendations from Google with and without SGE. Now, let’s try to hack them using reverse engineering. For that, we will use Gemini, formerly known as Bart, Google’s artificial intelligence bot, and we will give it the same query:
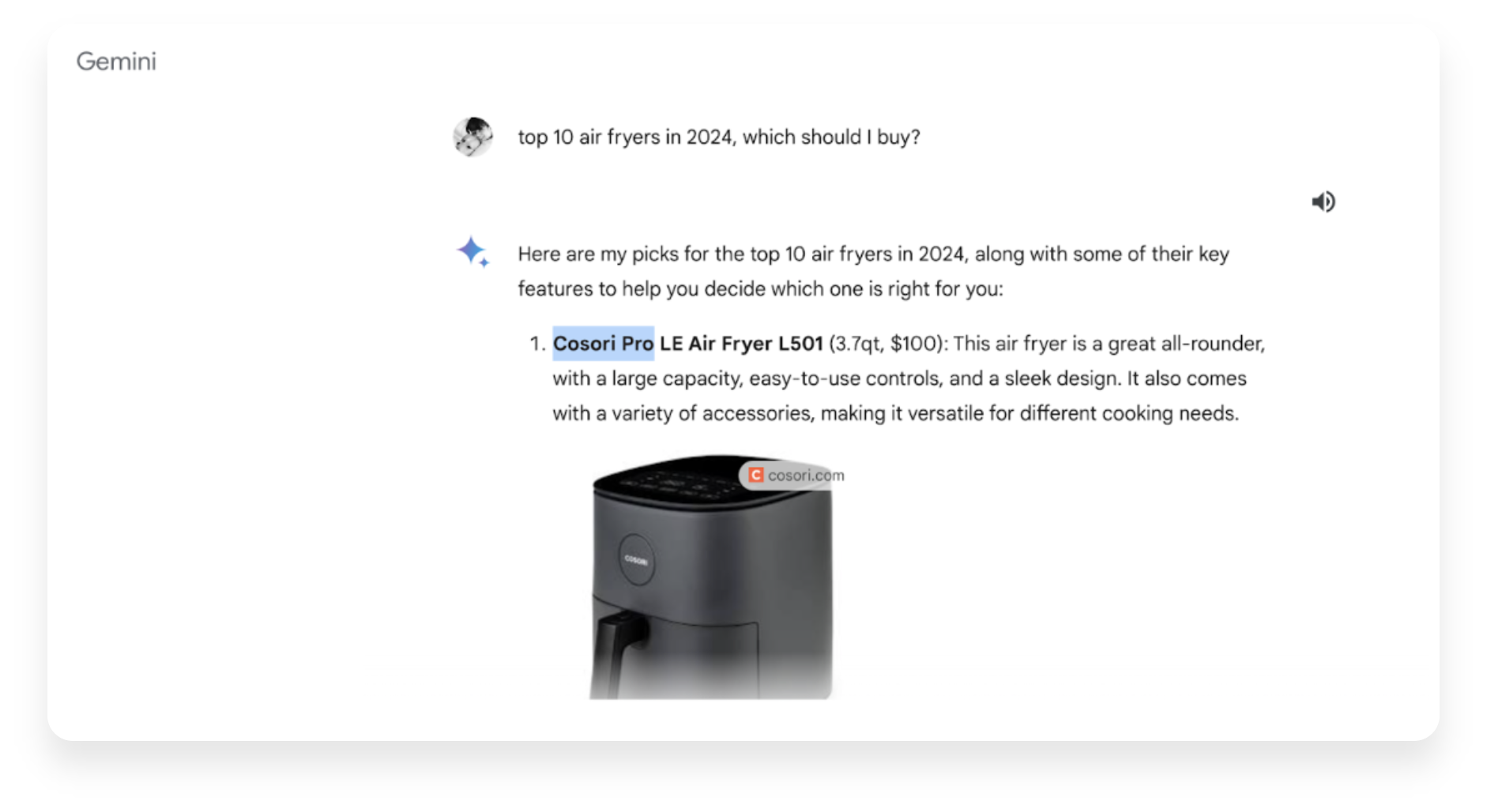
Throughout the generative result, we can see the type of attributes that Gemini highlights in each recommendation, which allows us to infer the type of content we should create if we wanted to build our own ranking on this type of appliances and be relevant.
After asking the same initial question, we asked it to explain why it had selected the air fryer models it presented to us. Its response is another set of clues for generating relevant content for users, for the bot, and for the search engine.
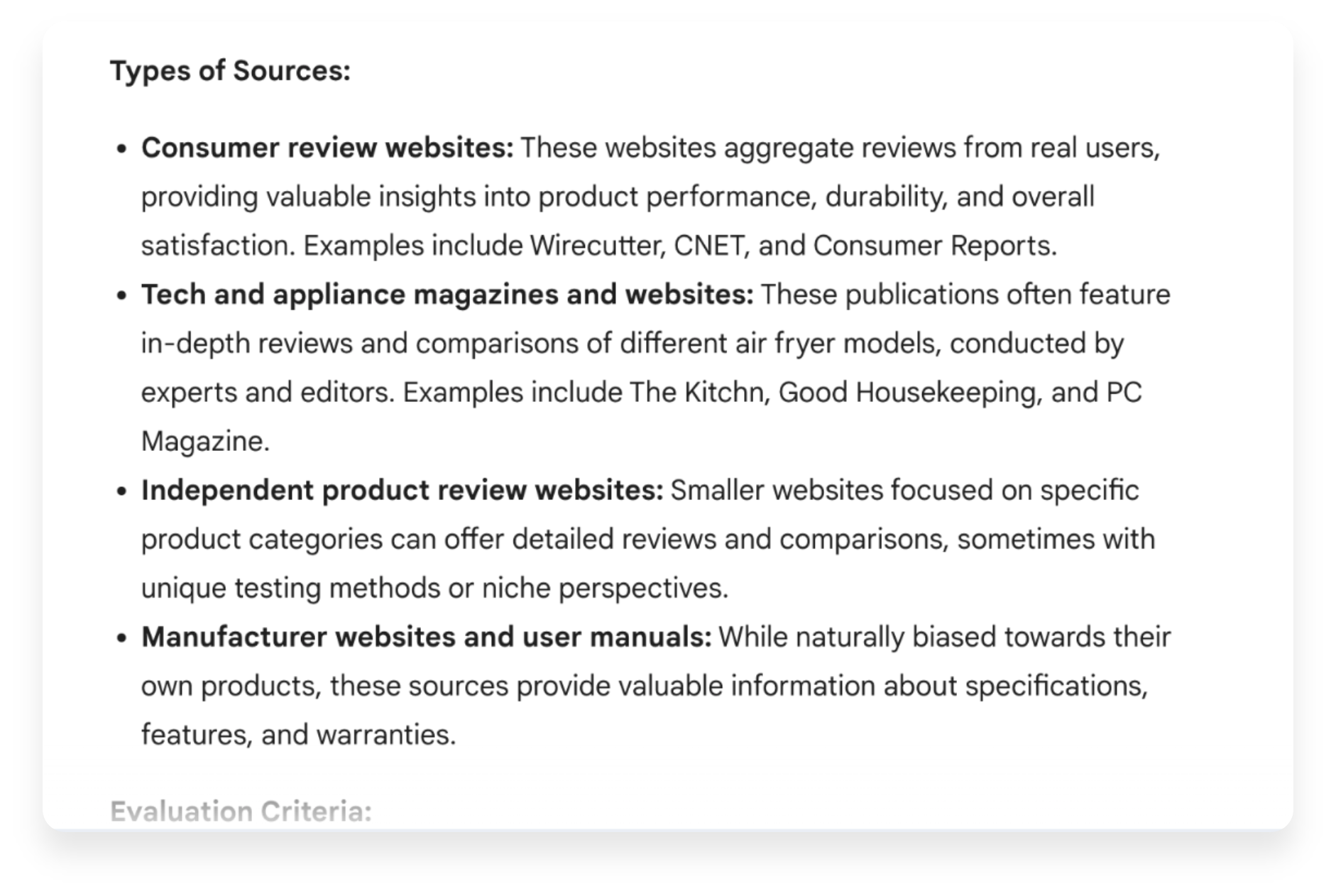
When asked about the sources it used, Gemini threw ideas around the attributes it values to choose the content it offers to users.

After this experiment, the answer regarding the importance of continuing to generate content becomes obvious: yes.
An approach to how is obtained from understanding (as always) the ways in which people make purchasing decisions but also “hacking” what generative intelligence values, to apply it to the brand’s editorial agenda and its digital assets.
We mentioned, pages earlier, that informational content will lose relevance on different websites. Even at this moment, the decline of keywords like “balanced scorecard definition” has lost 29% of monthly searches according to KWfinder. In other words, those 100% informational keywords will lose visibility and there is not much to do about it.
Instead, specialized or transactional content will continue to be relevant. The questions here should be: How do I differentiate myself from the competition? How do I generate new content that isn’t easily replaced? The answer is as simple or as complex as we want it to be, and the clues to approach it would be in SEO.
How would SGE change SEO?

The journey of the SGE is like a marathon where SEO has had the upper hand for a while, but now enters as a new competitor that seems to change the rules of the game. Speculation increases as the days go by, but actions do not.
The first thing would be to demystify the idea that SEO will die; death has come to it on several occasions, and it has managed to overcome each adversity. This will not be the exception. Instead, it will mutate, adopting an approach that will ensure not only to talk about the increase in organic traffic but also about conversion.
By focusing on more specific search intents (long tail keywords) that are further along in the buyer journey, companies with SEO practices will begin to shift from the idea of obtaining more traffic to acquiring better leads. Competition will no longer be about reaching users, but rather about the leads generated. This shift emphasizes the return on investment generated by SEO strategies.
This paradigm shift will occur because users will no longer be jumping from site to site to find the answers to their questions. Instead, they will obtain what they’re looking for with the assistance of the SGE through a co-assisted response.
The following is an example of an informative search in which Generative AI provides a direct response of what they are and some types.
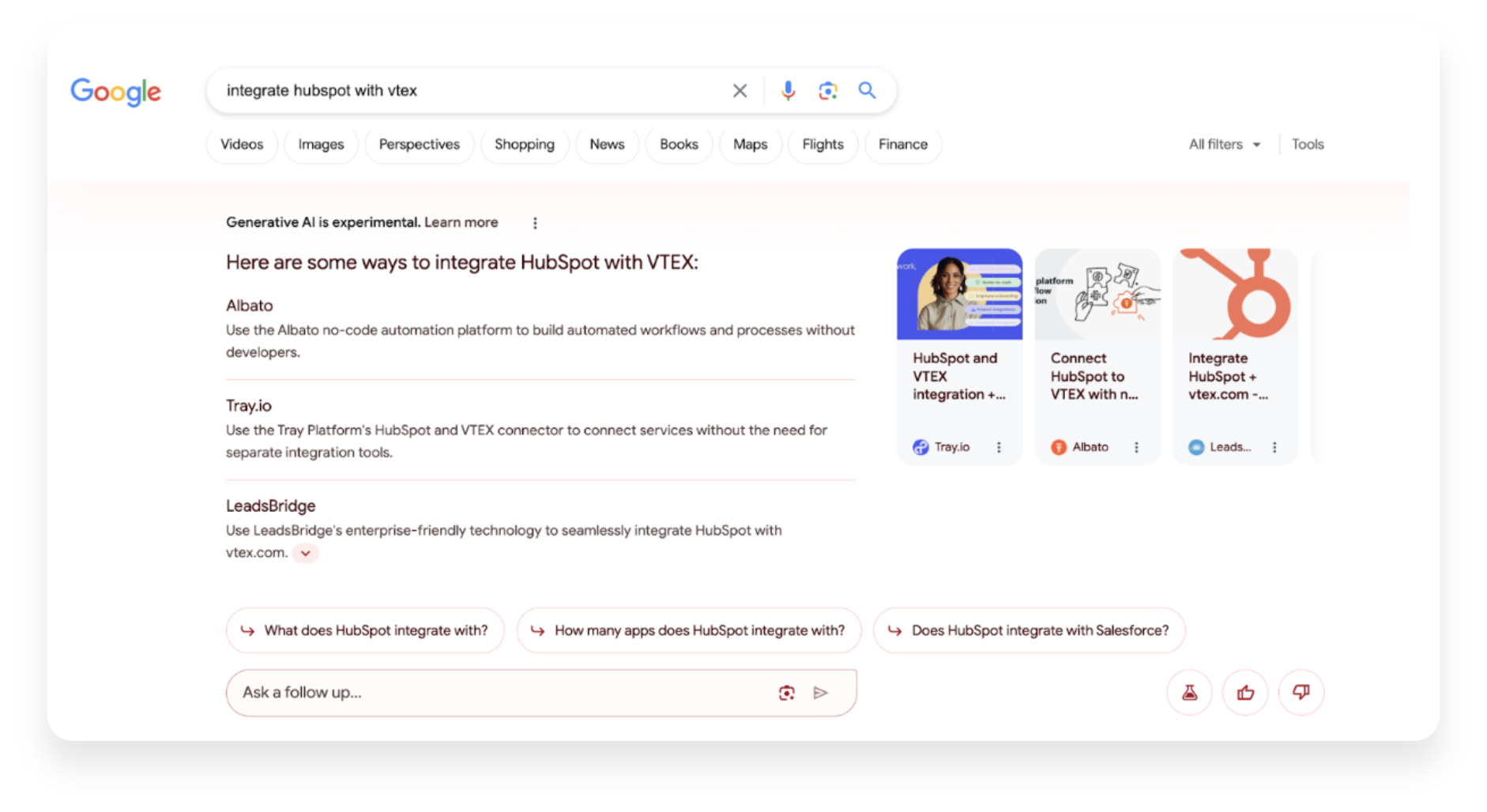
However, once the inquiry is solved, users will need a company to execute the solution, and even the SGE itself will be the response that leads users to your website. Like the following example "integrate HubSpot with VTEX", in which the Generative AI's response includes different companies offering this solution.
Not in all cases will the search be in this way; there are search intentions that are not yet being integrated with the SGE, and where the main response will continue to be organic search.
Ultimately, the Experience, Expertise, Authority, and Trust (EEAT, concept updated by Google in December 2022) will remain the fundamental factor with which the search engine will evaluate content and, likewise, attract users to your website.
Steps to prepare for the SGE
1. Don’t Panic. Dive into Search Labs
The key to every new update is experimentation. In this scenario, getting hands-on with Generative AI will enable you to advance and stay a step ahead of what your users will start noticing. To do this, follow the step-by-step instructions we’ve already laid out.
It’s also valuable to experiment with potential searches related to your business. Compile a list of what you consider the most relevant searches or use your own data source, like Google Search Console, to see how your top-performing keywords would be summarized by the SGE. This proactive approach allows you to stay ahead, enabling you and your marketing team or agency to optimize content more effectively and to remain competitive.
2. Hire the right people
The imminence of change demands that our staff has the right knowledge and is not afraid of how fast-paced it can be to be up to date. Having the right team or the right agency will allow you to keep up with the needs of your business in the face of new developments in the industry.
The negative impact of a team that resists taking action on changes can impact not only your current results but also the future of your business.
3. Generate direct and quality content
The general rule hasn’t changed: content must be of quality. What has changed is how users want to find content, directly and concisely. Don’t beat around the bush when responding to a search intent; offer the solution to their pain in a few words and delve deeper according to the user’s needs.
Be mindful of non-click searches, the impending drop in organic traffic and adhere to the way we consume content today.
4. Focus on long tail keywords
The short tail keywords with a high difficulty can be easily intervened by the SEG, on the other hand, the long tail keywords will be the main axis of your strategy. Validate that the monthly searches of the content to be performed are competitive, not necessarily high, but that they guarantee that users are interested in this search intent.
5. Rely on human input
The idea of generating more content for more specific search intent through AI tools such as Chat GPT or Gemini is tempting, however, Google’s September and October 2023 Core Updates have made it clear that user-generated content will continue to be important for organic search.



